Abstract
During hair transplant surgery, hair sampled from the nuchal area is implanted onto balding areas.
Hair transplantation was first performed in the 1930’s in Japan by Dr Issagawa, followed by Okuda and Tamura. In the 1950’s, the work of New-Yorker Dr Norman Orentreich popularized the technique of hair restoration and provided it with a scientific basis.
Hair transplantation has been through a lot of changes since it was first discovered. In 1952, Orentreich developed the technique of punch grafting, which remained the predominant hair transplantation technique until the 1980’s. The hair was sampled by groups of 20 to 30 using a round 3 mm to 5 mm punch. The sample was then transplanted onto the balding areas using the same instrument. This early technique of hair transplantation was characterized by a “doll’s hair” appearance, the donor area was peppered with circular “plug” scars.
In 1983, smaller grafts made their appearance; the circular sample was cut into halves or quarters and the grafts were implanted into recipient sites (round punch holes or scalpel slits) of equivalent size. From then on, samples became increasingly smaller, with minigrafts (4 to 5 hairs) and micrografts (1 to 2 hairs) making their appearance. The sampling technique was also improved on with the “strip” technique (Follicular Unit Strip Surgery or FUSS) coming into use. In this technique, a rectangular strip of scalp is sampled by the surgeon from the back of the head, leaving a thin scar. The technicians then cut the strips into slivers that are split into minigrafts and micrografts. The very small size of sample has made microscopic dissection a necessity.
In the 1990’s, Bobby Limmer popularized microscopic dissection of samples. The most recent technical advances have been made possible by the discovery of follicular units (FU). The sampling is mostly performed according to the FUSS (strip) technique. The technicians then split the samples into follicular units. The surgeon creates the recipient sites using needles or 1 mm blades. The follicular units (FU) or ultramicrografts are then implanted into the balding areas using very fine jewellers forceps.
Due to the increasingly small size of graft units, the number of grafts has had to increase in order to obtain a hair density similar to that of older techniques. With the 4 mm punch technique, a session of 50 grafts of 30 hairs each used to give a final transplant result of 1500 hairs; the first minigraft sessions were composed of 500 minigrafts of 3 hairs each, with the same final result of 1500 transplanted hairs. In 2006, sessions of 900 to 1200 minigrafts (i.e. between 2000 and 3000 hairs) are common, and so are sessions of 1000 to 2500 follicular unit grafts (i.e. 2300 to 6000 hairs). A large number of grafts and a high level of technical expertise are required in order to achieve a natural-looking final result. The procedure is performed by a team of 3 to 12 persons and can last from 3 to 12 hours.
The technique of Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) was first performed in Australia by Dr Wood, before being popularized by Drs William Rassman and Robert Bernstein and improved on by Dr James Harris. The sole distinctive feature of FUE lies in its sampling method using a 1 mm punch. Its main advantage is based on the microscopic size of scars in the donor area. FUE is of particular interest in cases of moderate baldness necessitating a small number of samples, especially in patients who want to keep their hair very short.
It should soon be possible to restore a large bald area in a single session of 7000 grafts. In the future, body hair may become a substitute to the remaining natural hair when the latter is in insufficient supply; nevertheless, cloning appears to be the foremost solution to the issue of donor area insufficiency. Although research is very active in this area, advertising and the media sometimes tend to promote techniques which haven’t yet proven their efficacy. Patients and hair surgeons must therefore exercise caution and put their trust in scientifically tested techniques only; close attention is needed in order to discriminate indisputable technical breakthroughs from simple marketing. This is not always easy and we hope that our work will bring helpful elements to operate this discrimination.
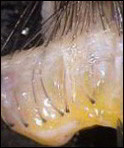
Photographies
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Strip
|
“Sliver” for minigraft
|
“Sliver” for follicular graft |
|
|||
|
Microscope
|
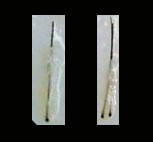
Micrograft and minigraft
|
Follicular unit grafts with 1 and
2 hairs |
Websites
http://www.emedicine.com/derm/topic559.htm
Hair Loss Learning Center
A multimedia rich site that enables visitors to share information and photos,
view animations and videos and learn about the elite members of the Coalition of Independent Hair Restoration Physicians.
http://www.hairlosslearningcenter.org
Hair Restoration Research Center
Provides in-depth expert articles on hair loss written by leading hair restoration physicians.
This site is sponsored by the Coalition of Independent Hair Restoration Physicians.
http://www.hair-loss-info.com
Hair Transplant Network
A popular and respected hair transplantation community dedicated to helping people share ideas and experiences about hair loss treatments and hair restoration physicians. This site includes hundreds of patient photos, a recommended “surgeon finder” and a popular hair loss discussion forum.
http://www.hairtransplantnetwork.com
Definitions
Cloning: Improperly used to indicate laboratory multiplication of hair from a hair sample. Follicular cell implantation would be a more appropriate term.
Donor area: The area of scalp providing graft samples for transplantation. It lies in the occipital and temporal areas along a band of hair circling the skull. This donor area is almost always present, even in very bald men. Sampling can be done using either a 0.7 to 1 mm punch in FUE technique or according to the strip technique.
Donor dominance: Dr Norman Orentreich demonstrated that the hair of the donor area (back and sides of the skull) that still remain in most bald men keep growing after they have been transplanted onto a bald area.
Double follicular unit: Graft containing two follicular units.
Follicular family unit: Two follicular units lying very close to each other.
Follicular isolation technique (FIT): Term coined by Drs Paul T Rose and John Cole to indicate the technique they designed for follicular unit sampling; specific type of follicular unit extraction or FUE.
Follicular unit: Hair is normally attached in the scalp in groups of 1 to 4 hair shafts; these groups are called follicular units.
Follicular unit extraction: Graft sampling technique using a 1 mm punch and allowing to extract a single follicular unit.
Follicular unit graft: Graft made up of a single follicular unit, i.e. 1 to 4 hairs (2.3 on average).
Micrograft: Each micrograft contains 1 to 4 hairs.
Minigraft: Small grafts mostly in use in the 1980’s but still largely used by some surgeons.
– Large minigraft (quadruple follicular unit): each minigraft contains from 6 to 12 hairs.
– Medium-size minigraft (triple follicular unit): each medium-size minigraft contains from 5 to 8 hairs.
– Small minigraft (double follicular unit): each small minigraft contains 3 to 5 hairs.
Multi-unit graft: Graft sample containing several follicular units.
Punch: Circular scalpel. Small metallic tube with a sharp end. A circular sample can be obtained by applying pressure on the tube whilst rotating it into the scalp. Dermatologists also use a punch to sample skin for microscopic analysis. Punch diameter varies according to the technique (from 0.75 to 10 mm): punch graft is performed with a 3 to 4 mm punch whereas follicular unit extraction uses a 0.75 to 1 mm instrument.
Punch graft: Graft sampling and transplanting technique using a 3 to 4 mm punch. Each graft contains from 15 to 30 hairs.
Quarter graft: Punch graft (3 to 4 mm punch) cut into quarters, each quarter graft containing 4 to 8 hair shafts.
Recipient area: Balding area where grafts sampled from the donor area are transplanted to.
Recipient site: Circular hole or slit created in the recipient area in order to receive the graft.
Safe System: Three-step FUE technique designed and patented by Dr James Harris.
Slit: Graft transplanting technique using a scalpel blade to create a slit in the recipient area.
Strip technique: Graft sampling technique in the shape of rectangular strips using either single-blade or multi-blade scalpel.
Triple follicular unit: Triple follicular unit graft or a graft containing three follicular units.
Abbreviations
FIT: Follicular Isolation Technique. Term coined by Drs Paul T Rose and John Cole to indicate the technique they designed for follicular unit sampling; specific type of follicular unit extraction or FUE.
FU: Follicular Unit. Group of 1 to 4 hairs naturally attached together with their sebaceous glands and arrector pili muscles.
FUE: Follicular Unit Extraction. Graft sampling technique.
FUSS: Follicular Unit Strip Surgery. Sampling of follicular unit grafts in the shape a strip. The term is used by Alvi Armani to indicate the strip sampling technique used in follicular unit grafts.
Mini: Minigraft.
Micro: micrograft.
MUG: Multi-Unit Graft. Graft sample containing several follicular units (2 or 3).
TFU: Triple Follicular Unit graft. Graft sample containing three follicular units.